CASE STUDY :
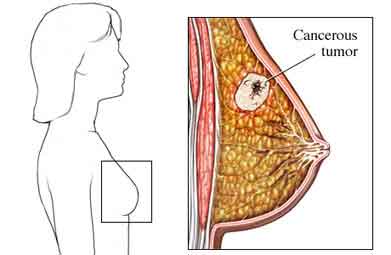
A recent case study found that increase use of antibiotics will significantly Increase the risk of breast cancer. Antibiotics affects our immune system by affecting its function and it also the function of inflammation. Antibiotics are drugs that are used to fight bacterial infections. Women with low or weakened immune system are mostly affected. Women who are at the age of 30-60 are most affected to this. But most of the doctors and scientist claimed that breast cancer is caused due to the damage of the breast cell but most of the antibiotics are not affecting the breast cell, though it has slighter chances of causing breast cancer.
It is important to remember that antibiotics prescribed by doctors to treat bacterial infections are still very safe and effective. But to know the truth we needed to do lot of research.
PESTICIDES
Most of the people think that cancer is caused because of improper nutrition, this is due to caused by the use of pesticides. Pesticide is also an antibiotic. DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) which is common pesticide found all over the world. But most of scientist has claimed that when women are exposed to it they developed a higher risk of developing cancer.
Pregnancy termination can also be a cause for the breast cancer. Because in pregnancy termination (abortion) the breast cells are damaged.
STRESS :
Various researches have been done to prove that stress is also a major reason for breast cancer. It is reported that women have been through some stressful condition are stated to develop a lump in the breast which later caused breast cancer.
Women with uneven boobs have the possibility of suffering from breast cancer this is due to the wrong use of antibiotics. The women with one breast larger and another smaller had suffered fatal and sever breast cancer.
People who take medicines for respiratory disease are found to develop breast cancer at a rate of 15%. And people who take medicines for skin are found to develop breast cancer at rate of 11% -14%. It is also proven that people who are exposed to antibiotics for more than 500 days are found to be have a elevated chance of breast cancer
CONCLUSION :
Utilisation of anti-infection agents is connected with expanded danger of episode and lethal bosom disease. It can’t be resolved from this study whether anti-infection use is causally identified with bosom tumour, or whether sign for use, general debilitated insusceptible capacity, or different components are relevant basic exposures. Albeit further studies are required, these discoveries fortify the requirement for reasonable long haul utilisation of anti-microbial.